Huawei OceanStor Dorado All-Flash Storage and Red Hat OpenStack
Interoperability Test Report

Axians Global All Rights Reserved
Executive Summary
Axians Global (“Axians”) assessed the interoperability of Red Hat OpenStack with Huawei OceanStor Dorado All-Flash Storage solution. The goal of the assessment is to validate that Red Hat OpenStack is interoperable with Huawei OceanStor Dorado All-Flash Storage.
In the assessment, Axians has determined that Red Hat OpenStack will function with Huawei OceanStor Dorado All-Flash Storage for the following scenarios:
Test Scenario | Storage Involved | Protocol(s) Tested | Result |
Basic Function Test | OceanStor Dorado All-Flash Storage | iSCSI | Passed |
Reliability Test | OceanStor Dorado All-Flash Storage | iSCSI | Passed |
The procedures conducted in the tests are referenced from standard online documentation from Red Hat OpenStack and Huawei.
1. Environment Configuration
1.1 Networking diagram
Figure 1.1 Huawei OceanStor Dorado Storage Test Networking Diagram
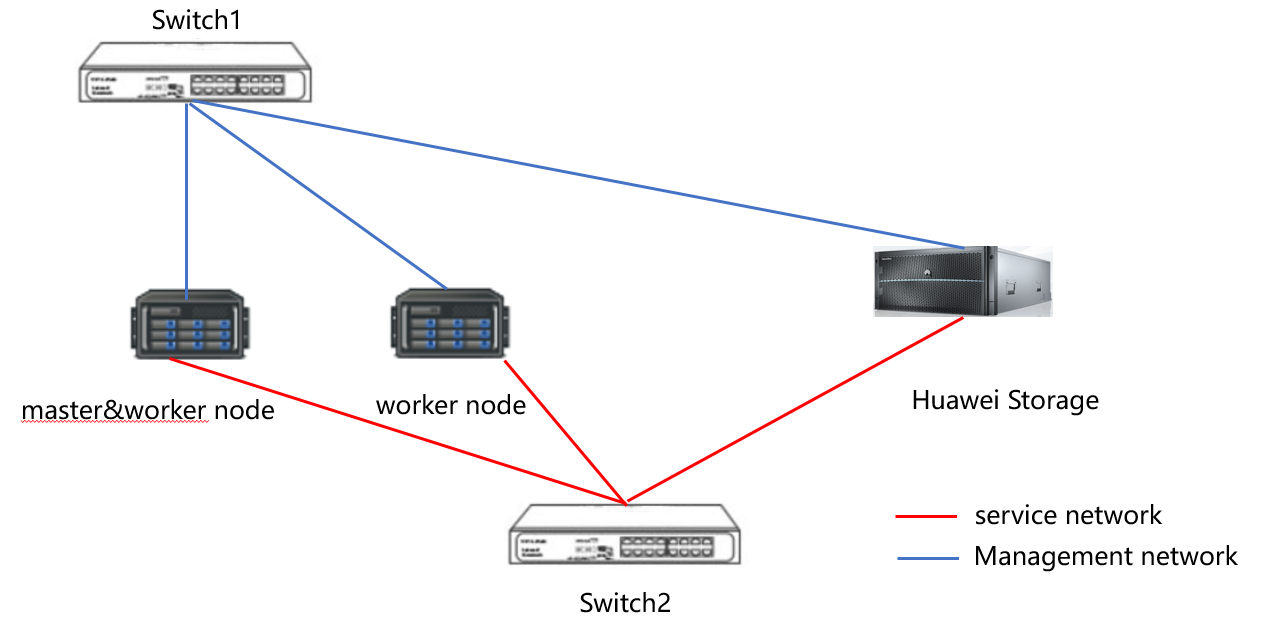
1.2 Hardware and Software Configuration
1.2.1 Storage Configuration
Table 1-1 Huawei storage configuration table
Name | Model | Version | Quantity |
Storage | Huawei OceanStor Dorado All-Flash Storage (Hereinafter referred to as “Dorado” as well) | V6 | 1 |
1.2.2 Matching Hardware Configuration
Table 1-2 Hardware Configuration
Name |
| Usage | Quantity |
| x86 server
| Deploy the VM for Red Hat OpenStack nodes. | 1 |
Ethernet switch | Huawei CE6855 10GE Network Switch | Ethernet switches for service and management networking. | 1 |
1.2.3 Test Software and Tools
Table 1-3 Test Software and Tool List
Software Name | description | Version | Quantity |
VMWare ESXi | VMware virtualization platform | 7.0 | 1 |
Red Hat OpenStack | A cloud platform management project | 16.2 | 1 |
| A plug-in deployed on the OpenStack Cinder module | 2.6.4 | 1 |
2. OceanStor Dorado Storage Interconnection with Red Hat OpenStack
2.1 Result Overview
The following table lists the overall test result.
Table 1-4 Test Result Overview
Total Cases | Pass | Pass with Comments | Fail | |
Result | 26 | 26 | 0 | 0 |
2.2 Result Details
The following table lists the result of each test case.
Table 1-5 Test Result Details
Test Case | Case Description | Result |
|---|---|---|
Creating a volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can properly invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to create volumes and generate corresponding LUNs on the storage system. | Pass |
Deleting a volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can properly invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to delete volumes and remove corresponding LUNs from the storage system. | Pass |
Deleting a volume in use | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack cannot delete a volume that has been attached to a VM. | Pass |
Deleting a volume with snapshots | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can properly invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to delete a volume with snapshots and remove the volume and snapshots from the storage system. | Pass |
Attaching a volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can attach a volume to a VM and invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to create the mapping between the host and the LUN on the storage system. | Pass |
Detaching a volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can detach a volume from a VM and invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to cancel the mapping between the host and the LUN on the storage system. | Pass |
Expanding the capacity of an available volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can expand the capacity of a volume in the available state and invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to expand the capacity of the corresponding LUN on the storage system. | Pass |
Expanding the capacity of an attached volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can expand the capacity of a volume in the in-use state and invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to expand the capacity of the corresponding LUN on the storage system. | Pass |
Suspending and recovering a VM | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can change the VM status from running to suspended and from suspended to running. | Pass |
Soft rebooting a VM | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can soft reboot a VM. | Pass |
Hard rebooting a VM | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can hard reboot a VM. | Pass |
Deleting a VM | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can delete a VM. | Pass |
Creating a snapshot for an available volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can create a snapshot for a volume in the available state and invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to create a snapshot for the corresponding LUN on the storage system. | Pass |
Creating a snapshot for an attached volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can create a snapshot for a volume in the in-use state and invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to create a snapshot for the corresponding LUN on the storage system. | Pass |
Deleting a snapshot | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can delete a snapshot for a volume and invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to delete the snapshot for the corresponding LUN on the storage system. | Pass |
Restoring a snapshot to a volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can roll back a volume using a snapshot and invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to roll back the corresponding LUN using the snapshot on the storage system. | Pass |
Creating a volume using a snapshot and mapping the volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can create a volume using a snapshot and attach the volume to a VM. The volume data is the same as that at the snapshot point in time. | Pass |
Deleting a volume created using a snapshot | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can delete a volume created using a snapshot. | Pass |
Creating a volume using another volume and mapping the volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can create a volume using another volume and attach the volume to a VM. The volume data is the same as that of the source volume. | Pass |
Deleting a volume created using another volume | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can delete a volume created using another volume. | Pass |
Creating an image | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can create an image and transfer the OS to the local storage or Huawei storage LUN. | Pass |
Deleting an image | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can delete an image. | Pass |
Hard rebooting a VM after the storage system is reset unexpectedly | To verify that the LUN mapping is normal and Red Hat OpenStack can hard reboot a VM after the storage system is reset unexpectedly. | Pass |
Powering off and recovering a controller (migrating and hard rebooting a VM) | To verify that the LUN mapping is normal and Red Hat OpenStack can hard reboot and migrate a VM after a storage controller experiences a power cycle. I/O reads and writes are normal after the storage controller recovers. | Pass |
IOPS volume type test | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to create a volume with IOPS limitations. | Pass |
Bandwidth volume type test | To verify that Red Hat OpenStack can invoke Huawei Cinder Driver to create a volume with bandwidth limitations. | Pass |
3. Reference
3.1 Red Hat OpenStack Documentation
https://docs.redhat.com/en/documentation/red_hat_openstack_platform/16.2